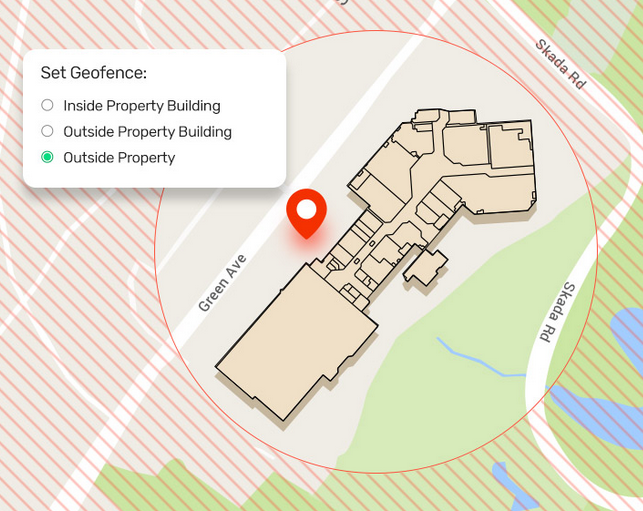
Whether home security geofencing is considered an invasion of privacy depends on several factors, such as the implementation, consent, and purpose of the geofencing technology. Let’s understand what Geofencing is.
What is Geofencing?
Geofencing in the context of home security refers to a virtual boundary created around a specific geographical area, such as your home, using GPS or RFID technology. This boundary is typically set up within a home security system or a smartphone app that is connected to the system. Geo-fencing can enhance home security by providing real-time information and automation based on the location of specific devices. It offers homeowners greater control over their security system and can help ensure that their property is protected even when they are away. When a device, such as a smartphone or a wearable, crosses the virtual boundary, the system can trigger various actions, such as:
- Sending Notifications: Homeowners can receive alerts on their smartphones or other devices when someone enters or exits the geo-fenced area. This can help them monitor activity around their property and identify potential security risks.
- Activating Security Features: Depending on the system, crossing the geofence boundary can automatically arm or disarm security features such as alarms, cameras, or smart locks. For example, when the homeowner arrives home, the system can recognize their device and automatically disarm the security system.
- Adjusting Smart Home Settings: Geo-fencing can also be used to control other smart home devices, such as adjusting lighting or thermostat settings based on the homeowner’s presence or absence. Adjusting smart home settings for geofencing typically involves using a smartphone app or web interface associated with your smart home system. The exact process may vary depending on the specific system, devices, and app you are using. Within the app, find the geofencing settings, and set up a virtual boundary around your home. You may need to enable location services on your smartphone to use this feature. Define the actions that should be triggered when you enter or exit the geofenced area. For example, you can set the thermostat to a specific temperature when you leave the geofence or have the smart lights turn on when you arrive home. Make sure to configure the settings for each device you want to control with geofencing.
Is Home Security Geofencing an Invasion of Privacy?
Whether home security geofencing is considered an invasion of privacy depends on several factors, such as the implementation, consent, and purpose of the geofencing technology. Here are some aspects to consider:
Consent and Awareness
If all members of a household are aware of and consent to the use of geofencing for home security, it may not be seen as an invasion of privacy. It is essential to have open communication with family members and ensure that everyone is comfortable with technology. Consent and awareness are crucial when implementing geofencing for home security to ensure that all members of a household understand and agree to its use. Here are some steps to help you establish consent and raise awareness when using geofencing technology:
- Open Communication: Discuss the use of geofencing technology with all household members, including family members, housemates, or anyone who may be affected by the system. Explain how the technology works, the benefits it provides, and the potential privacy concerns.
- Clear Guidelines: Establish clear guidelines and expectations for using geofencing technology. Define the purpose of the geofencing system (e.g., enhancing home security), the specific devices that will be tracked, and the actions that will be triggered when entering or leaving the geofenced area.
- Obtain Consent: Obtain explicit consent from all affected individuals before implementing geofencing for home security. Make sure everyone agrees to the use of this technology and is comfortable with it.
- Address Concerns: Address any concerns or questions that arise during the discussion. Ensure that everyone understands the implications of using geofencing, including data collection, location tracking, and possible privacy issues.
- Privacy Policy: Develop a privacy policy that outlines how the collected geofencing data will be used, stored, and protected. Share this policy with all household members to ensure transparency and trust.
- Regular Updates: Keep all household members informed about any changes or updates to the geofencing system. Discuss any new features, adjustments to the geo-fence boundary, or changes to data handling practices.
- Respect Preferences: Be sensitive to the preferences and concerns of all individuals affected by the geofencing system. If someone is uncomfortable with the technology or feels it is invasive, consider alternative methods of securing your home that do not involve geofencing.
Purpose and Scope
The intended use of geofencing technology is crucial in determining whether it is an invasion of privacy. If it is used solely for home security purposes and limited to the perimeter of the property, it is less likely to be invasive. However, if geofencing is used to track individuals’ movements beyond the property or for purposes other than security, it could be considered invasive. Geofencing can be integrated with security cameras or other surveillance systems to automatically activate or deactivate cameras based on the presence of authorized users within the geofenced area. Geofencing can send notifications to your smartphone or other devices when you or other authorized users enter or leave the geofenced area. This can help you keep track of family members’ movements and ensure their safety. Geofencing can be used to automatically notify emergency services, such as police or fire departments, when a security breach occurs within the geofenced area.
Third-party Involvement
If third-party companies or service providers have access to geofencing data, privacy concerns may arise. It is essential to understand the data sharing practices of any third-party companies involved in your home security system and ensure that they follow strict privacy guidelines. Here are some steps to help you evaluate the data sharing practices of third-party companies:
- Research the company: Gather information about the third-party company, including its reputation, history, and experience in the home security and geofencing industry.
- Read their Privacy Policy: Review the company’s privacy policy to understand how they collect, use, store, and share your data. Look for information about what types of data they collect, who they share it with, and how long they retain it.
- Data Sharing Agreements: Check if the company has data sharing agreements with other entities, such as partners, affiliates, or external service providers. Understand the purpose of sharing data and how the third parties handle the data.
- Data Protection Measures: Determine what security measures the company employs to protect your data, including encryption, access controls, and secure data storage. Look for adherence to industry standards and best practices.
- Opt-out Options: Look for options to opt-out of data sharing with third parties if you are not comfortable with their practices. Understand the implications of opting out and whether it might affect the functionality of your home security geofencing system.
- Transparency and Communication: Evaluate the company’s transparency and communication about their data sharing practices. A reputable company should be open and willing to answer any questions you have about their practices.
- Customer Reviews and Testimonials: Read customer reviews and testimonials to see if other users have experienced any issues with the company’s data sharing practices or have concerns about their privacy.
- Compliance with Regulations: Check if the company complies with relevant data protection regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union or the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the United States. Compliance with these regulations indicates that the company takes data privacy seriously.
- Regular Monitoring: Regularly monitor the third-party company’s data sharing practices and stay informed about any changes or updates to their privacy policy.
Data Collection and Storage
Home security geofencing involves collecting location data from devices. How this data is stored, who has access to it, and how long it is retained are crucial factors in determining the privacy implications. Implementing strong data protection practices and limiting access to the data can help mitigate privacy concerns. Here are some guidelines to help you ensure that your geofencing data is secure and protected:
- Encryption: Use encryption to protect data both in transit and at rest. This includes encrypting the data sent between your devices and the smart home system, as well as the data stored on servers or the cloud. Look for home security systems that use strong encryption standards, such as AES-256 or TLS/SSL.
- Strong Authentication: Use strong authentication methods, such as two-factor authentication (2FA), to protect access to your smart home system and app. This adds an extra layer of security by requiring a second form of verification, like a one-time code sent to your smartphone, in addition to your password.
- Regular Software Updates: Keep your smart home system and devices up to date with the latest software and firmware updates. These updates often include security patches that can protect your system from known vulnerabilities.
- Limit data retention: Retain geofencing data only for as long as necessary for its intended purpose. Periodically review and delete any data that is no longer required, and implement data retention policies to ensure data is not kept longer than necessary.
- Access control: Limit access to geofencing data to only those who need it. Use role-based access control (RBAC) to define the specific permissions and access levels for each user or group of users.
- Secure Data Storage: Store geofencing data securely, whether it is on a local server or in the cloud. Look for cloud storage providers that offer strong security measures, such as encryption, access controls, and regular security audits.
- Monitor and Audit: Regularly monitor and audit your home security system to detect any unauthorized access, data breaches, or other potential security issues. Set up alerts for suspicious activity, and investigate and address any incidents promptly.
- Educate Users: Ensure that all users of the home security system, including family members and housemates, are aware of the importance of data security and follow best practices for protecting their devices and accounts.
- Review Third-party Providers: If your home security system relies on third-party service providers, review their data handling and security practices. Ensure they follow strong data protection standards and have clear privacy policies in place.
In summary, home security geofencing can be invasive to privacy if not implemented carefully and with consent from all involved parties. It is essential to have transparent communication about the use of geofencing technology and ensure that it is used solely for the intended purpose of securing the home. Additionally, strong data protection practices and limited third-party access can help alleviate privacy concerns.